
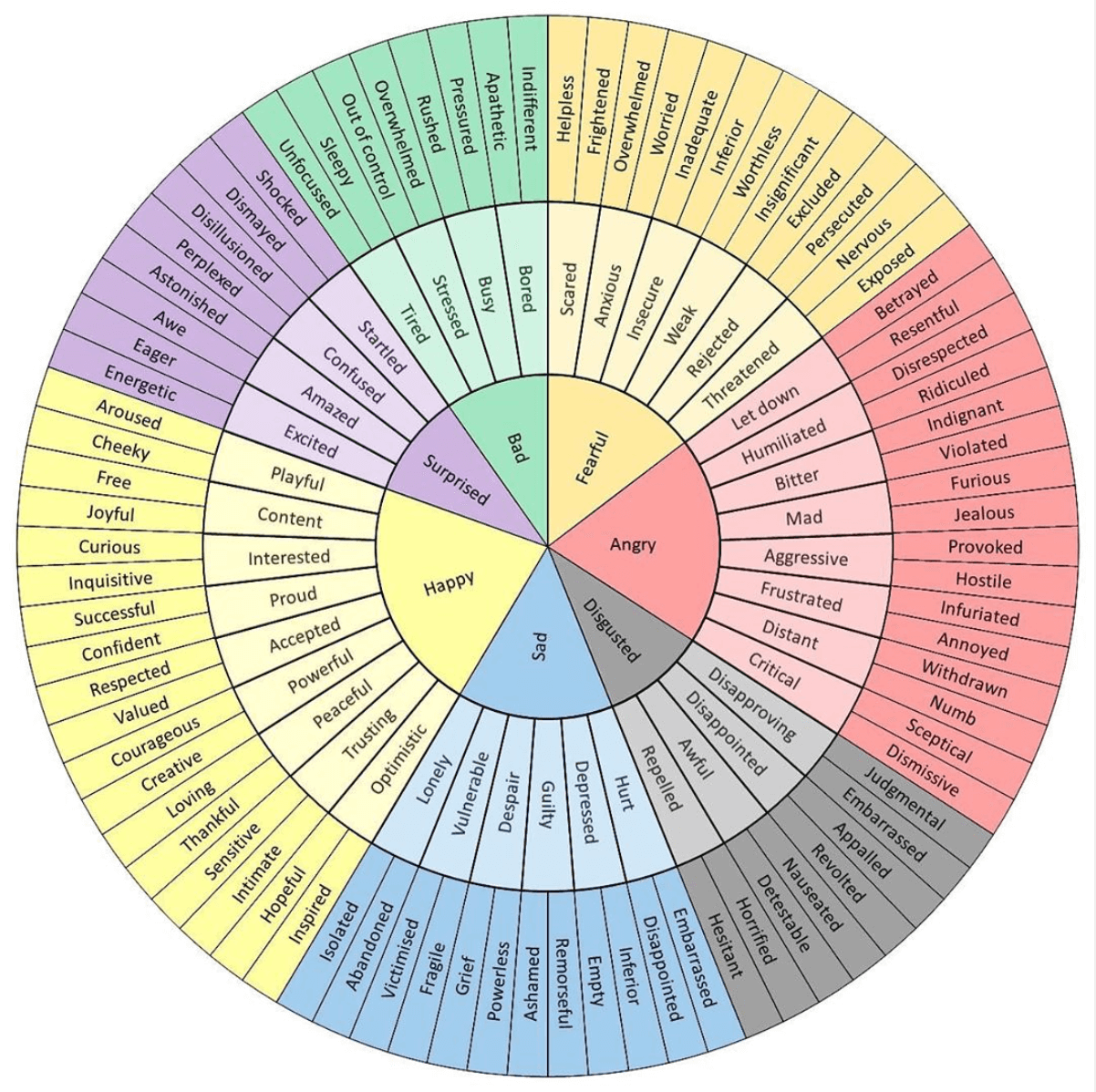
"The eight primary emotions in the emotion wheel are sadness, anger, disgust, joy, trust, fear, surprise, and anticipation," Espinoza explains. Through his psychoevolutionary approach, he asserted that our basic emotions play a role in human survival and can be patterned out to reveal common emotional elements that we all go through. Instead of casting emotions aside as too mysterious or vague for our interpretation, he wanted to understand their biological basis and the connections between them. To make it easier to recognize and describe our feelings, the wheel was gridded out in a way to demonstrate emotions in its various states, dyads, constructs, combinations, similarities, and dissimilarities. He believed that while humans have the capacity to experience over 34,000 unique emotions, there are eight primary, primordial emotions that serve as the foundation for other feelings, in all of their degrees and intensities, to exist and take place. Psychologist Robert Plutchik, Ph.D., created one of the most popular versions of the emotion wheel, a flower-shaped diagram to visually illustrate our emotions and their various, adjacent relationships to each other.

Alternatively students can create a fictional story in which the main character experiences the emotion. Invite students to describe a time when they felt a particular emotion. Use the wheel to spark creative writing.Begin conflict resolution with the statement “I feel….” Use the wheel as a classroom tool to help solve disputes.In pairs, have students compare their emotion wheels and brainstorm ways that the wheel could be used in the school setting or at home. Encourage students to expand their emotional vocabulary by searching the internet, thesaurus and using personal experiences.Ħ. Utilize colours to reflect the levels of intensity. Have them arrange the emotion words from mild to intense, with the most intense at the centre of the wheel. Invite students to add other emotion descriptors to the 8 categories of the wheel. Have them place each of the 8 chosen emotions on the wheel, arranging them so that they are next to emotions that they are related to, or closely connected with.ĥ. Individually, have students draw a wheel with 8 segments. The other groups can guess the emotion based on facial expressions, body language, or scenario if the actors are using words.Ĥ.
Secretly assign one emotion to each group and ask them to create a skit or mime to act out the emotion. Divide the class into eight small groups. Keep your choice of 8 emotions secret from the class until after the following step.ģ.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
